Role of Physical Fitness in Cerebral Palsy
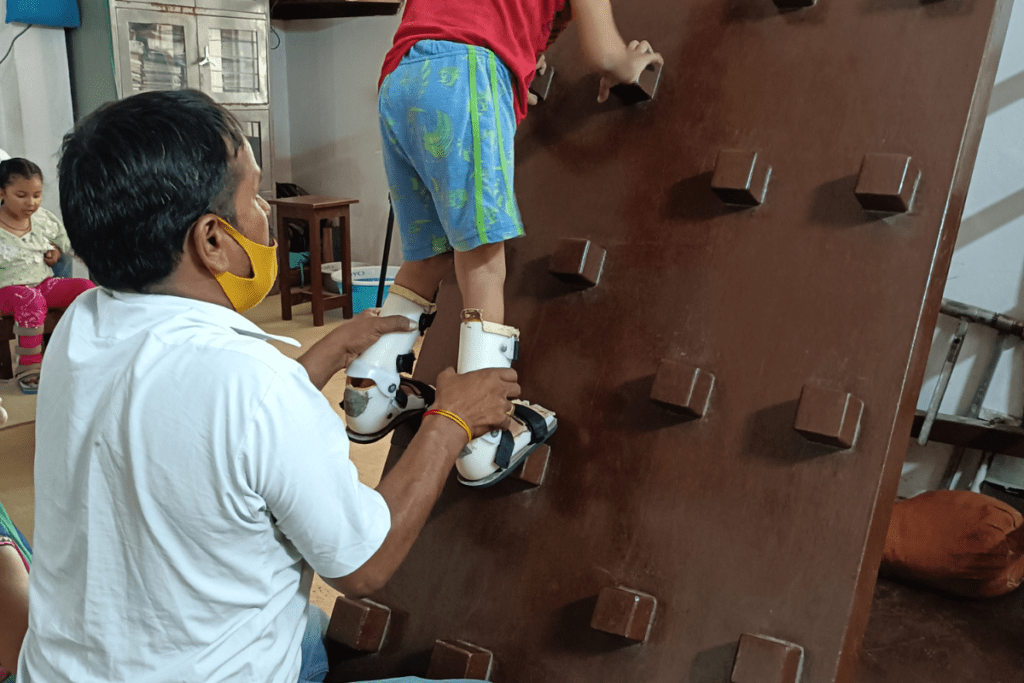

Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a neurological disorder that affects muscle control and movement. While there may not be a cure for CP, there are several ways to improve the quality of life for individuals living with this condition. One crucial aspect of managing CP is maintaining physical fitness. We will explore the significance of maintaining physical fitness, guide parents in encouraging their children toward wellness, discuss the ideal daily exercise routine for cerebral palsy children, and address some health challenges related to this condition.
Significance of Physical Fitness in Cerebral Palsy
Improved Mobility
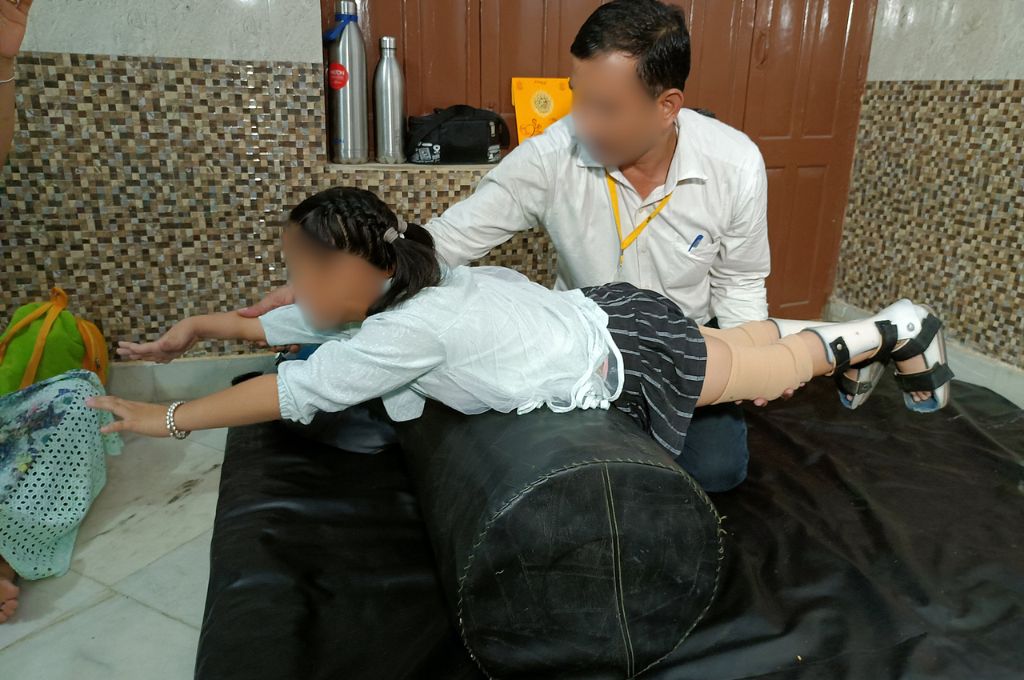
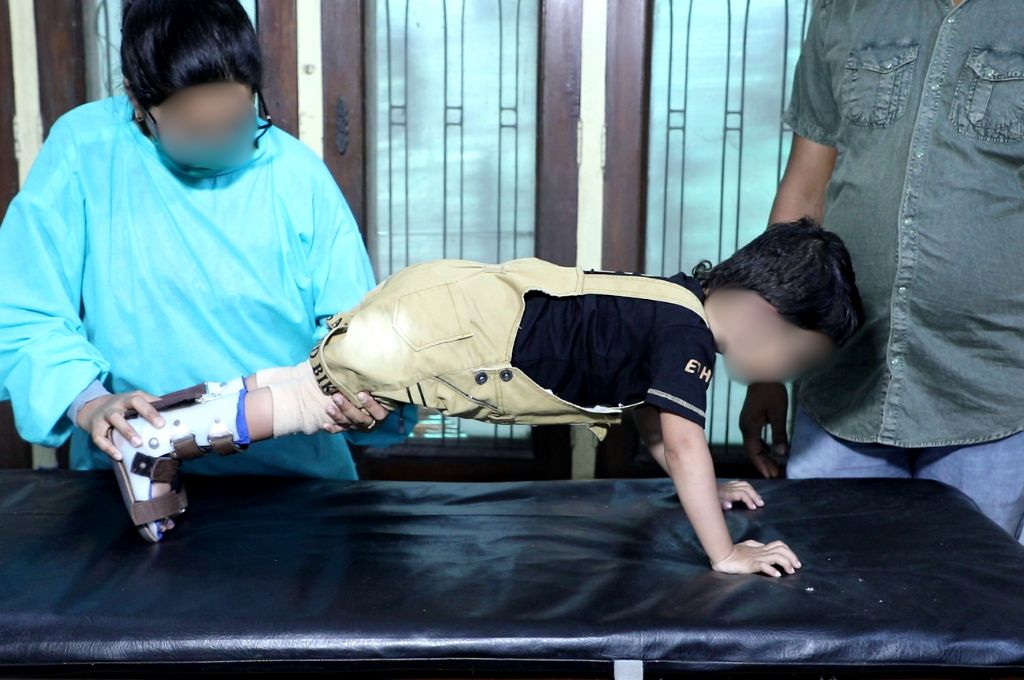
Children with CP often face muscle control and movement challenges. Maintaining physical fitness in cerebral palsy can significantly improve their mobility. Regular exercises help strengthen muscles and increase flexibility, making it easier for them to perform daily tasks like walking, standing, and reaching for objects.
Independence
Physical fitness in cerebral palsy plays a crucial role in fostering independence in children with CP. They can perform tasks without constant assistance as they become more robust and agile through exercise. This independence boosts their self-esteem and confidence.
Preventing Secondary Complications
Children with CP are at a higher risk of developing secondary complications, such as muscle contractures (permanent muscle shortening) and joint deformities. These complications can result from the limited range of motion and muscle tightness often accompanying CP. Physical fitness routines, which include stretching exercises, can help prevent or alleviate these complications.
Enhanced Cardiovascular Health
Maintaining cardiovascular fitness is essential for overall health. Children with CP may have limited opportunities for physical activity due to their condition. However, adapted aerobic exercises, such as swimming or using a handcycle, can help improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart-related issues.
Mental Well-being
Physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. For children with CP, who may face various challenges and limitations, regular exercise can contribute to improved mood and a reduction in anxiety or depression, promoting mental well-being.
Guiding Your Child Towards Wellness
Consult a Specialist
Before embarking on any exercise program for a child with CP, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals who specialize in treating individuals with this condition. They can assess your child’s needs and guide the most suitable exercises.
Individualized Plan
Each child with CP is different, and their exercise plan should be tailored to their abilities and goals. A physical therapist or rehabilitation specialist can help create a personalized fitness plan that addresses your child’s needs, whether improving balance, increasing muscle strength, or enhancing coordination.
Encouragement and Support
As a parent or caregiver, providing emotional support and encouragement is vital. Children with CP may face physical and emotional challenges during their fitness journey. Positive reinforcement and a supportive environment can help them stay motivated and committed to their exercises.
Consistency
Consistency is vital when it comes to physical fitness. Maintaining a regular exercise routine is essential to see meaningful improvements. Surface not only helps build physical strength but also establishes healthy habits. Incorporating various activities into your child’s fitness routine can keep them engaged and motivated. Boredom can be a barrier to exercise, so consider activities such as adapted sports, dancing, or other enjoyable physical activities that align with your child’s interests and abilities. Encouraging them to make friends also enables them to participate in these activities for a long.
What are the Ideal Daily Cerebral Palsy Exercises?
Range of Motion Exercises
Focuses on maintaining or improving joint flexibility. Stretching routines can help prevent muscle contractures and maintain a full range of motion. Gentle stretches or passive range-of-motion exercises can be part of a daily routine.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises target muscle groups to improve balance, stability, and overall muscle function. For example, the exercise plan can incorporate resistance band exercises or seated leg lifts.
Balance and Coordination Exercises
Balance and coordination are crucial skills for individuals with CP. Balance exercises, such as standing on one foot or using balance boards, can help improve postural control. Coordination can be enhanced through activities that involve hand-eye coordination tasks.
Aerobic Exercise
Low-impact aerobic exercises are beneficial for cardiovascular health. Swimming-adapted cycling, or using a hand, provides aerobic benefits without putting excessive strain on joints and muscles.
Adaptive Sports
Adaptive sports are inclusive and enjoyable because they are tailored to individuals with disabilities. These activities offer physical benefits and promote social interaction and teamwork. Examples include wheelchair basketball, adaptive yoga, and dance therapy.
Health Challenges
Spasticity
Spasticity is a hallmark CP symptom characterized by muscle stiffness and tightness. This can limit mobility and cause discomfort. Regular physical fitness routines that include stretching exercises, yoga & aerobic activities can help to manage spasticity and improve muscle flexibility.
Contractures
Prolonged muscle tightness can lead to contractures and permanent muscle shortening, resulting in joint deformities. Stretching and range-of-motion exercises are essential in preventing and managing contractures.
Pain Management
Chronic pain is common in individuals with CP due to muscle and joint issues. Physical fitness can alleviate pain by improving muscle function, circulation, and joint mobility.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Constipation and bowel problems are prevalent in children with CP. Physical activity can stimulate bowel movements and contribute to better digestive health. It’s essential to monitor nutrition and hydration as well.
Respiratory Challenges
Some individuals with CP may have difficulty breathing and lung function. Aerobic exercises that improve cardiovascular fitness can also enhance respiratory capacity, promoting better overall respiratory health.
Bone Health
Reduced bone density can be a concern in individuals with CP, leading to an increased risk of fractures. Weight-bearing exercises can help strengthen bones and mitigate this risk within the child’s capabilities.
Additional Tips for Parents
Proper Nutrition
Ensure your child receives adequate nutrition to support physical development. A balanced diet with essential vitamins and minerals is crucial.
Patience and Understanding
Progress may be gradual, and there may be setbacks along the way. Be patient and understand and celebrate even small achievements. A positive attitude can motivate your child to continue their fitness journey.
Seek Social Support
Joining support groups or connecting with organizations like the Trishla Foundation can provide valuable emotional support, information, and resources for parents and caregivers of children with CP.
Monitoring Overall Health
Keep a close eye on your child’s health, including regular check-ups with healthcare providers. Address any concerns promptly to ensure their well-being.
Goal Setting
Encourage your child to set achievable fitness and overall well-being goals. Setting and reaching these goals can be empowering and motivating.
Conclusion
Maintaining physical fitness is of utmost importance for children with Cerebral Palsy. It offers numerous benefits, including improved mobility, independence, prevention of secondary complications, enhanced cardiovascular health, and better mental well-being. By following healthcare professionals‘ guidance, providing support and encouragement, and designing an individualized exercise plan, parents and caregivers can help children with CP. He can lead healthier, more active lives. Understanding the specific health challenges related to CP and addressing them through appropriate exercise and care is vital for their overall well-being and quality of life.