Cerebral Palsy Diagnosis: A cerebral palsy is a group of neuro-motor disorders, which comprise difficulty in sitting, crawling, standing & walking along with other associated problems in speech, hearing, vision, recurrent chest infection, epilepsy, etc. Cerebral palsy occurs because of some insult to an immature brain of fetus in-utero, during delivery, and infant up to 2 years of life. Most of the time etiology of brain insult is unknown.
Cerebral palsy can be predicted at the time of birth with a history of high risk like very premature birth, very low birth weight & history of some insult to the brain like the history of hypoxia, delayed cry, severe jaundice, intrauterine infection.
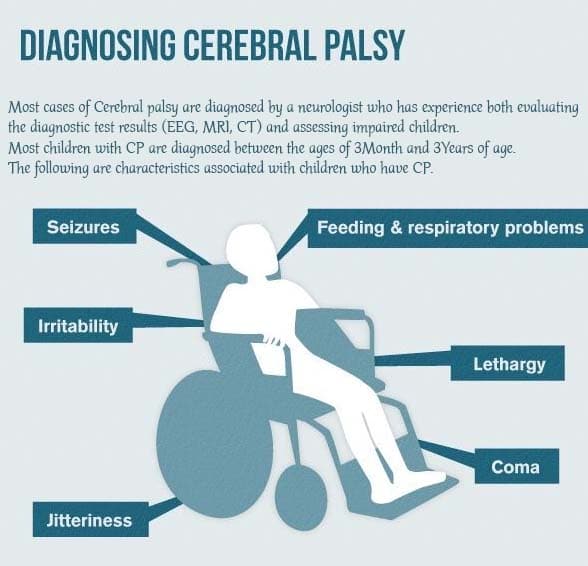
Observational Diagnosis:
In the first instance, it is very difficult to make the diagnosis & tell the parents about the possibility of cerebral palsy. There is no test which confirms the diagnosis. The majority of diagnoses can be made before the age of 1 year. But if the affection of cerebral palsy is mild then the diagnosis can be delayed.
How Soon Can A Diagnosis Be Made?
A definite cerebral palsy diagnosis can be made at 3-6 months of age with the history of abnormal social response, delayed in developmental milestone like the inability to take side turn & absent neck holding, abnormal/fluctuating tone of muscle like hypotonia/hypertonia, sucking problem, epilepsy, etc.
As the child matures other problems including achieving the milestone for a particular age like the inability to sit, crawl, walk, the problem in speech, vision, hearing, and persistence of infantile reflexes along with other medical problems can support the cerebral palsy diagnosis. MRI, CT scan of the head is required only to look for any pathology in the brain and in doubtful cases. Genetic analysis is required if suspected of some genetic cause. Metabolic assessment by blood investigation is required for evaluation of the metabolic cause of brain insult.
Diagnosis of cerebral palsy is being made on the basis of detailed history along with symptoms and signs. A detailed history from the parents is very important. Initially, we would like to know about delay in a developmental milestone in respect to age, social smile, difficulty in feeding, tone of muscle and posture, the persistence of abnormal primitive reflexes.
In history we would like to know mother condition during pregnancy, ANC checkup, immunization of mother, any adverse event at the time of birth, history of delayed cry, low birth weight, premature, infection, trauma, and aspiration in newborn.
Usually, neck holding is matured at the age of 3 months, sitting at 6 months, standing at 1 year, and walking capability at 13-14 months. If there is a gross delay in getting this milestone along with the history of some insult to the brain & high-risk history then the cerebral palsy diagnosis is confirmed.
Why Diagnosis Is Important?
Diagnosis is important for planning cerebral palsy treatment strategy & prognosis. Usually, diagnosis is being made by a pediatrician & some time by a pediatric orthopedic surgeon. Grandparents and parents are the key observers who help us in confirming the diagnosis.
Early diagnosis is very important for early intervention and guiding the parents because it gives rise to excellent outcomes in more than 80 % of children.
Diagnosis of cerebral palsy should include the status of gross motor functional level, fine motor activity, the severity of disability & associated medical problem.
Test To Cerebral Palsy Diagnosis:
Detail history & examination is sufficient to make a primary diagnosis. Most of the time investigation is not required but still, we need some pathological investigation in few children. Few scoring and assessment systems like GMFM scoring, house hand scoring, pediatric scoring are helpful in assessing the child clinically. Ultrasound brain is helping only in early infancy.
MRI:
MRI brain is required to see pathological changes in the brain and structural abnormality.
Metabolic Blood Investigation:
Metabolic blood investigation is required some time to rule out metabolic problems in children.
Genetic Evaluation:
Genetic evaluation is required to see the genetic abnormality in a child.
X-Ray:
X-ray of the pelvis is required to see hip dislocation & dysplasia.
X-Ray Foot:
X-ray foot is required to assess foot problems.
Blood Investigation:
A blood investigation is required to assess the thyroid, vitamin D, and general condition of the child.
Genetic Analysis:
Genetic analysis is required to assess the genetic causes of neonatal disability.
Differential Diagnosis:
It is very important to differentiate nonprogressive cerebral palsy from a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. In neurodegenerative disorders, the child will lose acquired milestones with the passage of time and disability will increase. In muscular dystrophy, the child will also deteriorate with aging. Muscular atrophy & fatty replacement of muscles will be marked in this problem.
Early Diagnosis & Treatment of Cerebral Palsy – Check Video
FAQ
1. At what age is cerebral palsy diagnosed?
The indications of cerebral paralysis normally show up in the initial month of life, yet numerous kids are not diagnosed until age 1 or later. Early symptoms of cerebral palsy include development delay, abnormal muscle tone, abnormal posture, etc. Now days with good observation we can predict the cerebral palsy even in child younger than 6 months of age.
2. How do you know if your newborn has cerebral palsy?
Here are some physical sign and symptoms that indicate cerebral palsy:
- Trouble in controlling speech-related muscles.
- Trouble doing a fine motor task such as writing.
- Difficulty in coordinating body movements.
- A child’s failure to lift their own head by the suitable age of development.
3. How do you diagnose cerebral palsy?
Diagnosing cerebral palsy (CP) at an early age is essential to kids and their families. Diagnosing cerebral palsy can take a various step:
- Developmental Monitoring: Tracking child growth & development
- Developmental Screening: Specific development delay in child
- Developmental and Medical Evaluations: Diagnose the particular type of disorder that influences a child.